
StudySmarter - The all-in-one study app.
4.8 • +11k Ratings
More than 3 Million Downloads
Free
Americas
Europe
Chemistry is about the tiny building blocks that make up everything in the universe! Briefly put, it is the study of the properties of matter. If you have ever wondered why the sky is blue or what makes a car move, then the answer has to do with chemistry. Chemistry is amazing, because it can explain simple everyday things from skincare to electricity to medicine.
Explore our app and discover over 50 million learning materials for free.












Lerne mit deinen Freunden und bleibe auf dem richtigen Kurs mit deinen persönlichen Lernstatistiken
Jetzt kostenlos anmeldenChemistry is about the tiny building blocks that make up everything in the universe! Briefly put, it is the study of the properties of matter. If you have ever wondered why the sky is blue or what makes a car move, then the answer has to do with chemistry. Chemistry is amazing, because it can explain simple everyday things from skincare to electricity to medicine.
 Fig. 1. Chemistry is everywhere in the world around you!
Fig. 1. Chemistry is everywhere in the world around you!
Chemistry is the study of the properties of matter, how matter changes and what it’s made of.
We can break down almost everything in the universe into tiny particles called atoms. There are 119 types of atoms in the universe. Groups of atoms bonded together are called molecules. In a chemical reaction, molecules rearrange themselves to make multitudes of materials and substances that exist today. Every material has a specific composition of atoms which we express as a chemical formula.
H2O is the chemical formula for water.
This means that a water molecule has two hydrogen (H) atoms and one oxygen (O) atom. Fig. 2. The chemical formula for water and its molecule.
Fig. 2. The chemical formula for water and its molecule.
In chemistry, you will learn the formulae for various materials and how to combine molecules in reactions. You will also learn how atoms make electricity and energy.
At StudySmarter you will find articles that cover topics at different levels of chemistry. You can make notes, add pictures, and use the handy articles written by our brainy content designers. They have included a ton of hints and tips to help you in your exams! You can also create your own flashcards and use the handy worked examples.
We sometimes call chemistry the central science because it combines maths, biology, physics and medicine, which is why chemistry has a number of branches. The topics covered in chemistry come under three main sections: Physical Chemistry, Inorganic Chemistry and Organic Chemistry. Let's have a brief look at what you’ll learn in each section.
You might have guessed that physical chemistry combines physics and chemistry.
As an example, let’s consider water. You already know its chemical formula: H2O. Now think about what happens when you boil water. How about when water freezes? Why does sugar dissolve in water? How does that happen? The chemical answers to these questions have to do with the arrangement of the atoms in a water molecule, while physics tells us what is going on between the water molecules.
 Fig. 3. The nature of the bond between the molecules gives water its unique properties, makeagif.com
Fig. 3. The nature of the bond between the molecules gives water its unique properties, makeagif.com
Essentially, physical chemistry is a study of how atoms behave. If you were to look into an atom you would see that it’s made of other tiny sub-particles called electrons, protons and neurons. Every atom has a unique arrangement of sub-particles (Atomic Structure). Atomic structure affects how atoms bond with each other (Atomic Bonding) and how they respond to heat (Thermodynamics). Some of the other topics under physical chemistry include:
Amounts of Substance
How do we count, measure and weigh atoms?
Bonding
How do atoms form bonds with each other?
Energetics
How does energy change in a chemical reaction? How do we use Hess’ Law to calculate the energy needed to make a compound?
Kinetics
How much energy do we need for a reaction to take place? Can we make a reaction happen more quickly?
Equilibria
Reactions that reverse themselves - how do they do this?
Redox
What happens in reactions that involve oxygen and hydrogen?
In 1869, a Russian chemist named Dimitri Mendeleev arranged all the known types of atoms to fit on what we now know as the periodic table of elements. Elements are the most basic materials in the universe. We can find carbon - the fourth most abundant element - in organic materials like wood, coal, and soil. Materials that do not have carbon in them are called inorganic compounds. So, inorganic chemistry is the study of materials that do not contain carbon. Have a look at the periodic table below - the pink element is carbon. That leaves a whole lot of other elements for you to discover in inorganic chemistry!
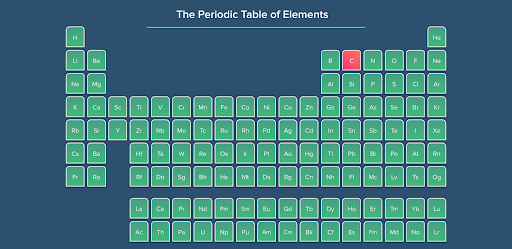 Fig. 4. Inorganic chemistry is the study of materials that do not contain carbon.
Fig. 4. Inorganic chemistry is the study of materials that do not contain carbon.
In inorganic chemistry, we will explore the periodic table. You will learn how we ended up with all the elements we see on it today and discover why Mendeleev arranged the elements that way. You will also learn about the similarities and differences in their properties, and how we use them in chemistry. The topics under inorganic chemistry include:
Periodicity and Trends
What is a group or period? What are the similarities between the elements in the same group or period?
Group 2
Why are the elements in the second column on the periodic table called alkaline earth metals? How do they react with oxygen and water?
Group 7
What are the different colours of the halogens? How do they react with hydrogen?
Period 3
What trends can you observe between the elements on the third row in the periodic table?
Transition Metals
What makes transition metals different from other metals on the periodic table? What are they used for?
Organic chemistry is the study of materials that contain carbon. ‘Organic’ means derived from living things. We call this field organic chemistry because scientists previously thought that we could only find organic compounds in living matter and they couldn’t be made artificially. Today, we know this is not true - we can manufacture numerous organic compounds in laboratories.
Even though organic chemistry mostly focuses on carbon, it is the second-largest section in chemistry. This is because carbon can combine with other elements to form a vast array of fascinating molecules, structures and compounds! Carbon bonds covalently with elements like hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen to make long complex repeating chains that form a variety of fantastic materials that we use today. Among the materials you will learn about in organic chemistry are alcohols and polymers. Other topics in organic chemistry include:
Alkanes
What do alkanes have to do with crude oil? How does carbon monoxide cause death?
Halogenoalkanes
What happens when a halogen reacts with an alkane? How do halogenoalkanes turn into alcohol?
Alkenes
What’s so special about the carbon bonds in an alkene? How do alkenes contribute to plastic pollution?
Organic Analysis
What techniques can you use to identify an organic compound?
Organic Synthesis
What are organic functional groups? How do you get from one to the other?
NMR Spectrometry
How do we use Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectrometry to analyse organic compounds?
Chromatography
What does chromatography have to do with dyes and forensic science?
Chemistry is a fascinating subject to study. You may find it challenging but each lesson will reward you with an understanding of the universe at a molecular level.
Flashcards in Chemistry10722
Start learningWhich statement is correct?
Protons have a relative mass of 1
Complete the following sentence: electrons are found ___________.
In shells orbiting the nucleus.
What does mass number represent?
The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom.
What does atomic number represent?
The number of protons in an atom.
Which particle determines the chemical properties of an atom?
Electron
Which particle determines the element an atom belongs to?
Proton
Already have an account? Log in
Open in AppHow would you like to learn this content?
How would you like to learn this content?
Free chemistry cheat sheet!
Everything you need to know on . A perfect summary so you can easily remember everything.
The first learning app that truly has everything you need to ace your exams in one place
Sign up to highlight and take notes. It’s 100% free.
Save explanations to your personalised space and access them anytime, anywhere!
Sign up with Email Sign up with AppleBy signing up, you agree to the Terms and Conditions and the Privacy Policy of StudySmarter.
Already have an account? Log in