
StudySmarter - The all-in-one study app.
4.8 • +11k Ratings
More than 3 Million Downloads
Free
Americas
Europe
GCSE Combined Science covers content from all three science subjects - Biology, Chemistry, and Physics - and earns you two GCSE qualifications. Unlike single science courses, Combined Science evaluates your performance across all three subjects. So if you’re looking for an all-rounder science qualification, Combined Science is the one for you.
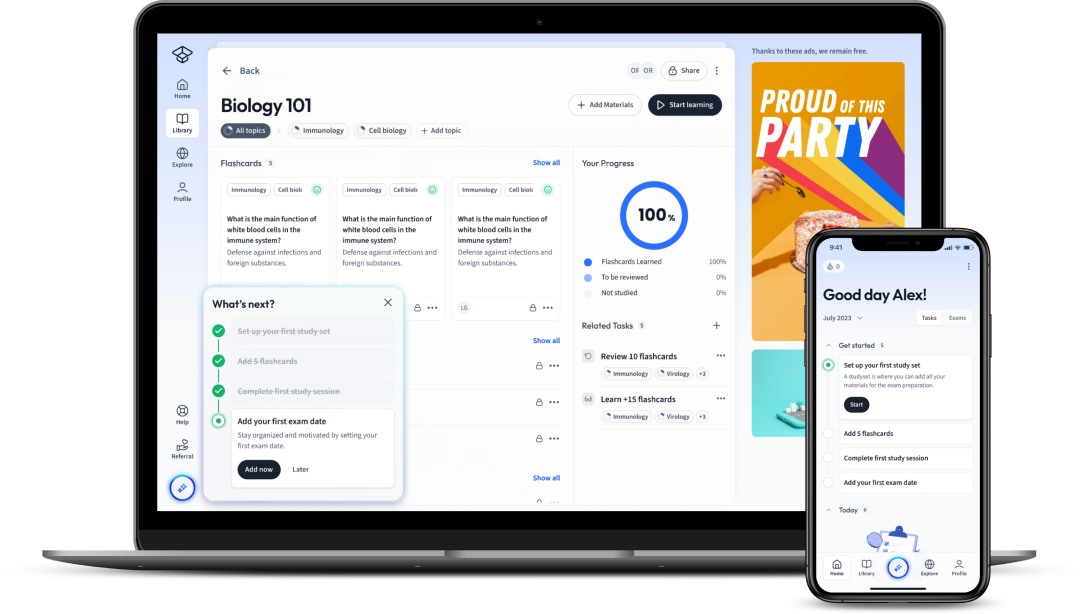
Explore our app and discover over 50 million learning materials for free.


Lerne mit deinen Freunden und bleibe auf dem richtigen Kurs mit deinen persönlichen Lernstatistiken
Jetzt kostenlos anmeldenGCSE Combined Science covers content from all three science subjects - Biology, Chemistry, and Physics - and earns you two GCSE qualifications. Unlike single science courses, Combined Science evaluates your performance across all three subjects. So if you’re looking for an all-rounder science qualification, Combined Science is the one for you.
Your Combined Science revision time can be easy and free! Your answer is StudySmarter, an award-winning study app offering an extensive collection of summaries, flashcards, notes, quizzes, and more, covering all Combined Science topics.
The StudySmarter app can be used online and offline at no cost to you. That’s correct; StudySmarter is a free study app.
Here’s why you should start your comprehensive Combined Science exam prep with StudySmarter:
✔ Easy access to thousands of flashcards in Combined Science topics - or you create your own directly from your study material!
✔ Free expert-verified summaries for your GCSE prep, such as Cell Organelles and Human Impact on Climate Change.
✔ An intelligent study plan, complete with analytics and a study timer, to motivate you to pass your Combined Science and all other exams.
✔ Create study groups to share documents, notes, and flashcards. Perfect for a team project or a group study session!
And so much more! With StudySmarter, learning is accessible and fun!
 Easy access to thousands of flashcards in Combined Science topics.
Easy access to thousands of flashcards in Combined Science topics.
Combined Science Synergy and Trilogy are two different approaches to teaching science at the GCSE level. Synergy is a more general approach that covers the basics of biology, chemistry, and physics. Trilogy is a more in-depth approach covering more topics in the three sciences.
In Synergy, the content of biology, chemistry, and physics is combined into one course. This means that students learn about all three sciences together and see how the different subjects are related. Synergy is a good option for students who want to get a broad overview of science.
In Trilogy, the course is split into three sections. Each one tackles the three different sciences: biology, chemistry, and physics. The majority of the content and key practicals overlap with the individual science GCSEs. Trilogy is a good option for students who want to specialize in a particular science.
Did you know that science experts at StudySmarter meticulously crafted Combined Science explanations covering all relevant topics, available free of charge?
Develop scientific knowledge and understanding across biology, chemistry, and physics with explanations and flashcards on topics such as Building Blocks of Science, the Evolution of the Atmosphere, and the Conservation of Mass.
Combined Science and Triple Award Science are both GCSE courses that cover biology, chemistry, and physics. However, the main difference is that Combined Science is worth two GCSE qualifications, while Triple Award Science offers students the opportunity to gain three separate GCSEs in each subject.
Triple Science covers more in-depth material and is ideal for students interested in pursuing science-based careers or further studies in these subjects. On the other hand, Combined Science is a good option for students who want to gain a broad understanding of science but may not want to specialize in a specific area.
Combined Science | Triple Science |
Biology: Cells, tissues, organs, and systems; reproduction; inheritance; evolution; ecology | Biology: Cells, tissues, organs, and systems; reproduction; inheritance; evolution; ecology; genetics; microbiology |
Chemistry: Atoms, molecules, and bonding; structure and properties of matter; chemical reactions; energy changes | Chemistry: Atoms, molecules, and bonding; structure and properties of matter; chemical reactions; energy changes; organic chemistry; inorganic chemistry; physical chemistry |
Physics: Forces and motion; electricity and magnetism; waves and sound; light and heat | Physics: Forces and motion; electricity and magnetism; waves and sound; light and heat; mechanics; thermodynamics; electromagnetism; nuclear physics |
When choosing between Combined and Triple Science, you should consider the following factors:
Your interests and future plans. If you are interested in pursuing a career in science, Triple Science may be a better option as it will give you a more in-depth understanding of the subject. However, if you are not sure what you want to do after GCSEs, Combined Science may be a better choice as it is less demanding and allows you to explore other subjects.
Your ability in science. If you are good at science, Triple Science may be a good challenge for you. However, if you find science difficult, Combined Science may be a better option.
Your workload. Triple Science is a more demanding course than Combined Science. If you are already struggling with your workload, Combined Science may be a better choice.
Your school’s offer. Not all schools offer Triple Science. If you want to take Triple Science, you will need to check if your school offers it.
It is important to choose the right course for you. If you are not sure which course to choose, talk to your teacher or a career advisor. They can help you make the best decision for your future.
Combined Science, also known as Double Science, is a GCSE qualification that involves the study of all three major science subjects, including Biology, Chemistry, and Physics.
Combined Science, also known as Double Science GCSE, covers all three science subjects including Biology, Chemistry, and Physics. However, it is a combined course that results in students receiving two GCSE qualifications, which is where the name "Double Science" comes from.
The percentage of students who take triple science varies among schools. In 9% of schools, all students take three sciences; in 4% of schools, most classes take three sciences, and in 21% of schools, a minority of classes take three sciences, such as only the top set. Usually, students are given a choice of whether to study three sciences, although this option may not be available to all students.
Combined Science grades are calculated by adding together all marks from the science exams and setting seventeen grade boundaries. This results in two grades that may not be at the same level but could be adjacent. For example, a student may receive a 6-5 or a 5-4 for their combined science grades.
Flashcards in Combined Science1871
Start learningDefine osmosis in terms of water potential.
Osmosis is the movement of water molecules down a water potential gradient, through a semipermeable membrane.
What is the water potential of pure water?
0kPa.
What are the three types of tonicity?
Hypotonic, isotonic and hypertonic.
Compare plant cells placed in a hypertonic solution to plant cells placed in a hypotonic solution.
In a hypertonic solution, plant cells will undergo plasmolysis and will become flaccid.
But in a hypotonic solution, planning cells will become turgid and firm.
Compare animal cells placed in a hypertonic solution to animal cells placed in a hypotonic solution.
In a hypertonic solution, animal cells will become crenated and shrink.
But in a hypotonic solution, animal cells will undergo cytolysis (cell bursting).
Under what tonicity do plant cells and animal cells perform best?
Plant cells perform best in hypotonic solutions.
Animal cells perform best in isotonic solutions.
Already have an account? Log in
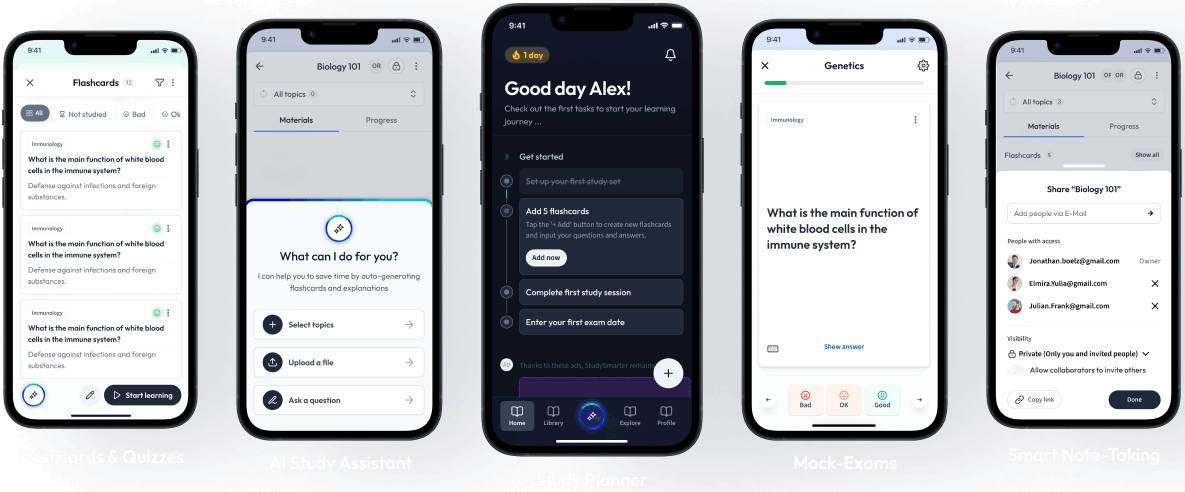
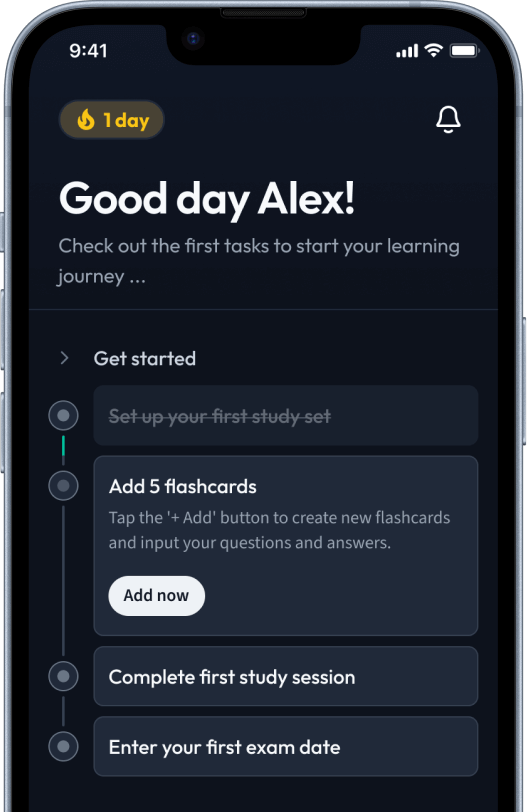
Open in AppHow would you like to learn this content?
How would you like to learn this content?
Free combined-science cheat sheet!
Everything you need to know on . A perfect summary so you can easily remember everything.
The first learning app that truly has everything you need to ace your exams in one place
Sign up to highlight and take notes. It’s 100% free.
Save explanations to your personalised space and access them anytime, anywhere!
Sign up with Email Sign up with AppleBy signing up, you agree to the Terms and Conditions and the Privacy Policy of StudySmarter.
Already have an account? Log in