
StudySmarter - The all-in-one study app.
4.8 • +11k Ratings
More than 3 Million Downloads
Free
Americas
Europe
If someone were to ask you what biology was, how would you reply? Biology is quite a complex concept to explain. Does it study plants, animals and humans only, or does it cover much more than that?
StudySmarter’s Biology Revision and Notes will show you that biology is the study of life. In fact, it is the study of ALL life and even some things that are classified as not living – viruses, for instance. Biological study starts from the smallest atoms and molecules, such as carbon atoms in the proteins that digest our food. Biology then examines larger structures, such as tissue, organs, and whole organisms, including bacteria, viruses, plants, animals, and humans. It continues with the study of topics including genetic diversity, the evolution of species, and ecosystems.
Explore our app and discover over 50 million learning materials for free.


























Lerne mit deinen Freunden und bleibe auf dem richtigen Kurs mit deinen persönlichen Lernstatistiken
Jetzt kostenlos anmeldenIf someone were to ask you what biology was, how would you reply? Biology is quite a complex concept to explain. Does it study plants, animals and humans only, or does it cover much more than that? StudySmarter’s Biology Revision and Notes will show you that biology is the study of life. In fact, it is the study of ALL life and even some things that are classified as not living – viruses, for instance. Biological study starts from the smallest atoms and molecules, such as carbon atoms in the proteins that digest our food. Biology then examines larger structures, such as tissue, organs, and whole organisms, including bacteria, viruses, plants, animals, and humans. It continues with the study of topics including genetic diversity, the evolution of species, and ecosystems.
Our planet Earth is one massive, incredible ecosystem! It is packed with various forms of life, from the smallest microorganisms to plants and large animals. These forms of life interact with one another; they move, reproduce, and live in oceans, grass, cities, villages, etc. Imagine you are standing on the top of a mountain, looking down at all this diversity. That is all included in the study of life, i.e. biology. Impressive, isn’t it?
On StudySmarter, you will find vital resources for your biology courses. We follow specifications developed by expert teachers of biology. This way, we ensure our content is high-quality and relevant to all who embark on a learning journey with StudySmarter. Most biology courses cover the following topics:
Biological molecules.
Cells.
Substance exchange.
Genetic information.
You’ll find those on StudySmarter, but we also offer you these topics as well:
Energy transfers.
Responding to change.
Genetics, populations, evolution and ecosystems.
Control of gene expressions.
Let’s introduce all the biology topics.
Biological molecules are carbon-based compounds essential for most biological processes.
Biological molecules serve as the structural components of molecules and cells, such as simple carbohydrates in bases of DNA and RNA and complex carbohydrate cellulose in plant walls. Moreover, biological molecules called lipids build cell membranes, forming a phospholipid bilayer. Some biological molecules, like proteins, act as enzymes, messengers and hormones, carrying out metabolic functions. Nucleic acids, DNA and RNA, carry the genetic information in all living things and viruses. The other two essential biomolecules are ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and water, necessary for cellular processes.
 Diagram of a molecule. Source: Canva
Diagram of a molecule. Source: Canva
Cells are the smallest units of life. The study of cells is one of the most significant in biology.Cells can be either prokaryotic or eukaryotic. They contain genetic material and divide to create new cells. Eukaryotic cells divide with processes called mitosis and meiosis. Prokaryotic cells divide by binary fission.
Cells vary in the number and type of organelles, which are subunits inside all cells. One of the essential structural components of the cell is the cell surface or plasma membrane. It serves as a protective layer and is the main player in transporting vital substances in and out of cells. Specialised cells called T lymphocytes and B lymphocytes are crucial for our immune systems. These cells aid in the fight against diseases.
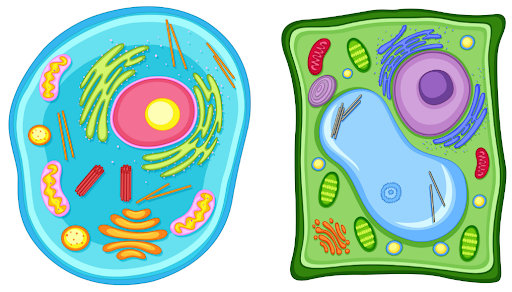 Eukaryotic cells: an animal cell and a plant cell. Source: Freepik.com by brgfx.
Eukaryotic cells: an animal cell and a plant cell. Source: Freepik.com by brgfx.
Substance exchange in biology is the exchange of substances (e.g. glucose) between the internal and external environments of cells.
This is how organisms get oxygen and nutrients from the external environment and get rid of metabolic waste. Multicellular organisms require specialised organ systems for substance exchange because their surface area to volume ratio is too small to rely on cell membranes as an exchange surface.
Substance exchange in plants is called a mass flow system. The mass flow systems of plants comprise xylem and phloem. Substance exchange in animals happens in different organ systems, including the digestive, respiratory, and circulatory systems. Digestion and absorption of nutrients occur in the digestive system, whereas gas exchange takes place in the respiratory system. The circulatory system pumps and circulates blood that carries nutrients and oxygen. This role of the circulatory system is crucial to ensure the high metabolic activity of cells for all of the organ systems in the body to function properly.
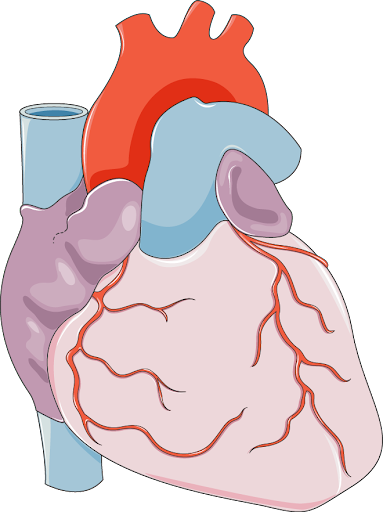 Diagram of the human heart. Source: smart.servier.com
Diagram of the human heart. Source: smart.servier.com
DNA is a remarkable molecule consisting of our genetic material. Genetic material is involved in every aspect of biology, making DNA an essential molecule for the continuation of life.
The DNA in the nucleus is organised into genes made of nucleotides, which are found on chromosomes. Sometimes, the order of these nucleotides goes wrong, and mutations occur. Different mutations have different effects on the organism, but one of the beneficial effects is introducing genetic diversity into a species. Genetic diversity is also achieved during meiosis (a type of cell division) which allows DNA to be switched around so that the sex cells (also called gametes) have a different combination of DNA.
As a result of this vast genetic diversity in organisms, we have millions of species that we need to organise and classify. This is the study of taxonomy. Complementary to genetic diversity is the biodiversity we see in communities. We can quantify this level of diversity using measurements such as the index of biodiversity and species richness.
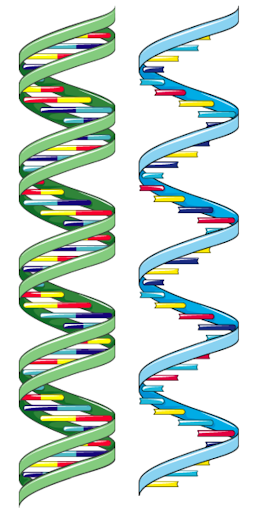 DNA and RNA. Source: smart.servier.com
DNA and RNA. Source: smart.servier.com
The term energy transfer refers to the changes in energy that occur in and between organisms within an ecosystem.
All life depends on energy, which is usually derived from the Sun. The transfer of this energy between different organisms allows them to maintain their highly ordered environments and communities.
When it comes to how energy is transferred, there are two types of organisms: autotrophs, including plants, lichens or algae, and heterotrophs, including animals and humans. Most autotrophs gain energy from the Sun via photosynthesis. This process involves autotrophs using light energy to turn carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen. Heterotrophs cannot synthesise their own energy and rely on acquiring it through consuming other organisms. They perform an inverse process to photosynthesis: they take glucose and oxygen and turn them into carbon dioxide and water. This energy transfer is called respiration.
 Plants use the energy from the Sun for photosynthesis. Source: Canva
Plants use the energy from the Sun for photosynthesis. Source: Canva
Organisms respond to change in the internal and external environments. The change comes in the form of a stimulus. The stimuli (singular stimulus) can be a physical or chemical change and are recognised by specialised cells called receptors. The response to the stimuli is crucial for the survival of species. Neurones or nerve cells are cells specialised for transporting nerve impulses. There are millions of neurones in mammals, making up the complex and fascinating nervous system. Some of the organs coordinated by the nervous system are the muscles. Contraction of skeletal muscles starts with an action potential reaching and travelling deep into muscle fibres, ultimately triggering the sliding filament mechanism. All these responses to changes are necessary for the body to maintain a constant internal environment. This is called homeostasis. Living organisms require a consistent temperature, pH, and an overall chemical balance to function.
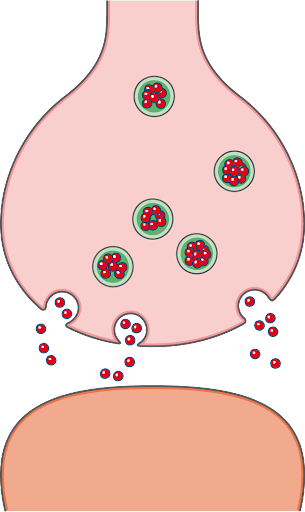 Diagram of a synapse and the transmission of nerve impulses. Source: smart.servier.com
Diagram of a synapse and the transmission of nerve impulses. Source: smart.servier.com
Individual members of one species have the same set of genes but can vary in combinations of alleles. Alleles are different forms of a gene responsible for the genetic diversity in species. The more alleles in the genome of a species, the greater the genetic diversity. When members of one species live together in a habitat, they form populations. These, in turn, form communities where diverse species cohabit and interact with one another. The population size can vary and is affected by biotic (living) and abiotic (non-living) factors. For instance, competition and predation within or between different species are biotic factors, while the pH and temperature in the species’ habitat are abiotic factors.
Communities and the environment they inhabit make up ecosystems. An ecosystem is a self-sustaining, dynamic system that includes all living organisms (biotic part of the ecosystem) and the physical environment (abiotic components).
 A varied ecosystem with animals, plants and their habitat. Source: Freepik.com by macrovector
A varied ecosystem with animals, plants and their habitat. Source: Freepik.com by macrovector
Some of the DNA in our cells can contain mutations. Considering all cells start off with the same genome, how can they have different functions and features, i.e. mutations? It is because of different levels of gene expression. Some genes in the genome are switched ‘on’, meaning they are expressed, and the proteins they code for are made, while other genes are switched ‘off’, meaning the corresponding protein is not synthesised.
Mutations can affect the level of expression, but epigenetics also plays a significant role. Epigenetics investigates the modifications made to DNA and their associated proteins and how this affects the level of gene expression. Other influencing factors include processes happening before transcription and before and after translation.
These investigations into DNA and genes require remarkable gene technologies, which have been used to develop advanced medical techniques such as gene therapy and forensic technology such as genetic fingerprinting.
 A scientist investigating DNA and genes. Source: Canva
A scientist investigating DNA and genes. Source: Canva
Whether you are revising the topics covered in your biology course or studying for your upcoming exams, StudySmarter has got you covered. Our original, efficient, smart, and interactive learning system allows you to master biology like never before. What’s more, it’s all free! What is the secret? How do we do it? To find out more, follow our Biology Revision Guide.
 pch.vector at freepik.com, edited in Canva
pch.vector at freepik.com, edited in Canva
Our intelligent guide is here to introduce everything you need to know to revise your biology courses and exams successfully. Here is what you can discover on StudySmarter:
StudySmarter biology summaries cover all you need to know about essential topics in biology, introducing interesting facts that will deepen your understanding and appreciation of the subject. Did you know that a human heart goes through a cardiac cycle that is only 0.8 seconds long?You can also become a creator yourself by uploading your biology coursework: summaries, workbooks, notes, and more.
Flashcards are a fantastic feature helping you learn in an easy and fun way. Biology flashcards contain questions and answers on topics covered in the summaries. Did you know that you can create your flashcards with particular questions YOU want to practice? How cool is that!
You don’t have to stop at creating and uploading your material. StudySmarter lets you form study groups and learn with your friends and biology students from wider learning communities. Remember the flashcards? You can use them to quiz fellow group members and test their knowledge. This way, you can create a personalised Biology quiz! Learn, create, quiz – repeat.
StudySmarter is your next best friend, encouraging you to learn and achieve top results. StudySmarter lets you set your weekly goals: complete subjects, correctly answer flashcards, ask questions. Reaching these goals will earn you trophies. For example, gain the Best thing since sliced bread if you study every week for three months, or become a Grandmaster if you answer five questions in the same course. The more you learn, the more trophies you get to celebrate your hard work.
 StudySmarter trophies: earn while you learn!Source: Freepik.com by makyzz, edited in Canva
StudySmarter trophies: earn while you learn!Source: Freepik.com by makyzz, edited in Canva
Our StudySmarter Biology Team is made up of subject-matter experts with knowledge of and experience in teaching, learning, writing, and research related to biology and related sciences. The Biology Team is always hard at work, working diligently and enthusiastically to bring you easy-to-understand explanations of complex topics that are tailored to your courses and exams in biology.
Let's meet the Biology Team!
Biology Team Lead | |
Laura Sotillos | Laura holds a Masters in Neuroscience, and is an expert in the intersection of genetics and psychiatry, as well as a lover of Nature. |
Biology Subject-Matter Experts | |
João Aguiar | João has a Master of Science in Molecular Medicine and is interested in everything related to molecular and synthetic biology. |
Charlotte Berdat | With a master's degree in Biochemistry, Charlotte is an expert in ethnobotany and all things disease aetiology. |
Quisha Bustamante | Quisha has a bachelor's degree in Biomedical Sciences and is an expert in infectious diseases and pathogens. |
Lillian Bieszke | Lillian has her bachelor's degree in Biosystems Engineering and focuses mainly on biomedical engineering. |
Isadora Santos | Isadora has a bachelor's degree in Biology (with a focus on Microbiology) and a special interest in fungi. |
Daniela Lin | Daniela, who has a bachelor's degree in Microbial Biology, is a fan of data visualization, graphic design, and computational genomics. |
Xavier Gagné | With a Bachelor of Science in Geology, Xavier is an expert in hydrogeology, soils, and environmental health. |
Nicole Reasonda | Nicole has a Bachelor of Science in Community Development, and she focuses specifically on psychology and neuroscience. |
Tiarnán McKeever | Tiarnán is currently a medical student, and he has a special interest in psychiatry. |
Victoria Harper-Alexander | Victoria is currently completing her PhD in Biomedical Science (she has a Master of Science in Molecular Biology and Neuroscience) and is passionate about bioinformatics and virology. |
Agastya Sharma | Agastya has a Bachelor of Science in Marine Biology with a special interest in animal biology. |
Odeta Razmaite | With a master's degree in Marine Science, Odeta has an interest in the environment, conservation, and all things marine, especially marine invertebrates. |
Flashcards in Biology13828
Start learningBoth DNA and RNA are _____ acids.
Nucleic.
Compare the functions of DNA and RNA.
DNA stores genetic information while RNA transfers this genetic information for protein synthesis.
Where is DNA found in the cells of eukaryotes and prokaryotes?
In eukaryotes, DNA is in the nucleus, mitochondria and chloroplast (in plants).
In prokaryotes, DNA is in the nucleoid and plasmids.
Where is RNA found in the cells of eukaryotes and prokaryotes?
In eukaryotes, RNA is in the nucleolus and ribosomes.
In prokaryotes, RNA is in the nucleoid, plasmids and ribosomes.
Identify the three different types of RNA.
Messenger RNA (mRNA), transfer RNA (tRNA) and ribosomes RNA (rRNA).
What nitrogenous bases can DNA nucleotides have?
Adenine, thymine, cytosine or guanine.
Already have an account? Log in
Open in AppHow would you like to learn this content?
How would you like to learn this content?
Free biology cheat sheet!
Everything you need to know on . A perfect summary so you can easily remember everything.
The first learning app that truly has everything you need to ace your exams in one place
Sign up to highlight and take notes. It’s 100% free.
Save explanations to your personalised space and access them anytime, anywhere!
Sign up with Email Sign up with AppleBy signing up, you agree to the Terms and Conditions and the Privacy Policy of StudySmarter.
Already have an account? Log in