
StudySmarter - The all-in-one study app.
4.8 • +11k Ratings
More than 3 Million Downloads
Free
Americas
Europe
Have you ever found yourself floundering in the dense sea of algorithms, coding languages, and digital logic, wondering how to navigate through your A-Level Computer Science course? Fret not! StudySmarter illuminates the path to success with straightforward explanations and interactive flashcards, meticulously designed to transform your revision experience.
Explore our app and discover over 50 million learning materials for free.














Lerne mit deinen Freunden und bleibe auf dem richtigen Kurs mit deinen persönlichen Lernstatistiken
Jetzt kostenlos anmeldenHave you ever found yourself floundering in the dense sea of algorithms, coding languages, and digital logic, wondering how to navigate through your A-Level Computer Science course? Fret not! StudySmarter illuminates the path to success with straightforward explanations and interactive flashcards, meticulously designed to transform your revision experience.
Imagine an app that doesn't just bombard you with information, but instead breaks down complex computer science concepts into digestible segments. We make revision more manageable by providing tailored resources, be it understanding the inner workings of an operating system or untangling the intricacies of Python programming. You can also find out whether you have a future in computing with our overview of Computer Science university degrees and jobs.
Your Computer Science revision time can be easy and free! Your answer is StudySmarter, an award-winning study app offering an extensive collection of summaries, flashcards, notes, quizzes, and more, covering all Computer Science topics.
The StudySmarter app can be used online and offline at no cost to you. That’s correct; StudySmarter is a free study app.
Here’s why you should start your comprehensive Computer Science exam prep with StudySmarter:
✔ Easy access to thousands of flashcards in Computer Science topics - or you create your own directly from your study material!
✔ Free expert-verified summaries for your A Level prep, such as Computer Programming and Algorithms.
✔ An intelligent study plan, complete with analytics and a study timer, to motivate you to pass your Computer Science assessments and all other exams.
✔ Create study groups to share documents, notes, and flashcards. Perfect for a team project or a group study session!
And so much more! With StudySmarter, learning is accessible and fun, and can even bridge the gaps between A Level and your journey to a University degree.
The following modules are free the moment you sign onto our free app:
| Module Number | Area of Study |
| 1 | Computer Programming |
| 2 | Data Structures |
| 3 | Algorithms |
| 4 | Theory of Computation |
| 5 | Data Representation |
| 6 | Computer Systems |
| 7 | Computer Organisation and Architecture |
| 8 | Issues in Computer Science |
| 9 | Computer Network |
| 10 | Databases |
| 11 | Big Data |
| 12 | Functional Programming |
| 13 | Problem-Solving Techniques |
A Level Computer Science is a UK-based pre-university level qualification in the field of computing. Designed for you if you're between 16 and 19 years old, the curriculum broadly covers computing methodologies, data structures, algorithms, software development, and data representation.
In an A Level Computer Science Course, you'll be exposed to both theoretical concepts and practical applications. These can range from programming languages, databases, to cybersecurity principles. This comprehensive curriculum forms a strong foundation for you to establish your future career in various computer science fields.
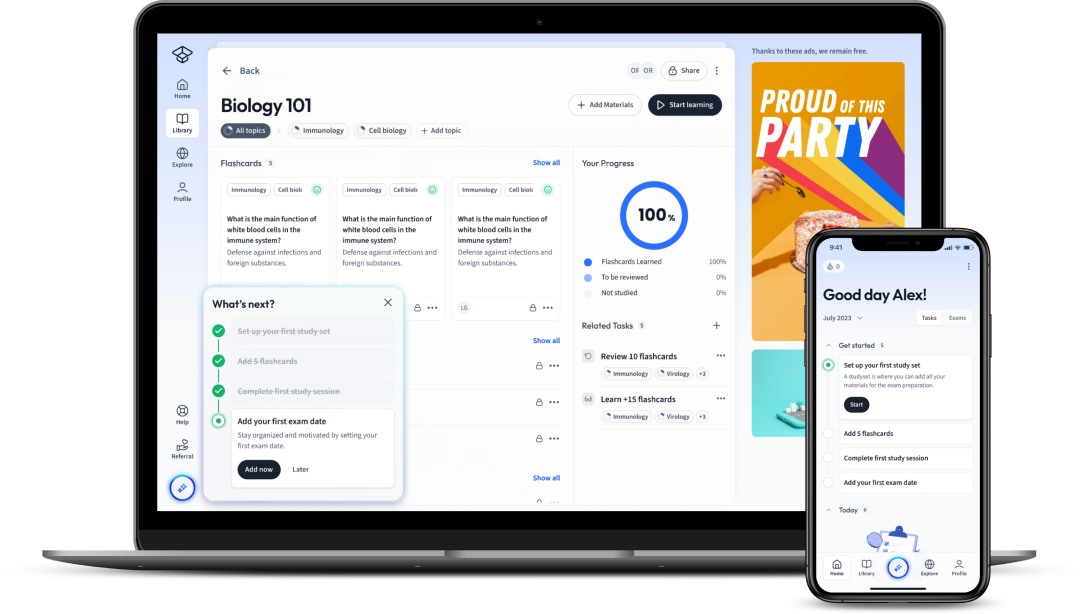
 Fig. 1 - StudySmarter offers easy-to-understand explanations for your Computer Science Revision.
Fig. 1 - StudySmarter offers easy-to-understand explanations for your Computer Science Revision.
Digging deeper into the content of an A-Level Computer Science course, you'll study a series of modules. These modules will introduce you to a variety of computer science principles and applications.
As a student, you'll learn:
As part of your A-Level Computer Science course, you'll be assessed on your practical capabilities, alongside your theoretical knowledge.
This often involves an independent programming project that you are required to complete. By the end of your course, you should be able to:
A Computer Science Degree course at a university broadens the scope of your knowledge. It covers a wider array of topics, delving much deeper into each one compared to A-Level Computer Science. Within a degree course, you'll study a variety of modules comprehensively. These typically include advanced programming, data analysis, artificial intelligence, machine learning, and much more.
Here are some of the key topics that you are likely to study in a Computer Science Degree:
Having a Computer Science Degree can open a wealth of opportunities for you in the job market. These qualifications are highly sought after by employers, particularly those in the tech sector.
As a graduate, your specialist knowledge and skills can apply to a wide range of roles, including:
Choosing the right university to study Computer Science can play a big part in your career success. The best universities offer extensive resources, leading faculty, and strong industry links.
Here are several of the best universities worldwide for studying Computer Science:
Each of these universities offers world-class Computer Science programmes that are highly respected globally.
When choosing a university to study Computer Science, consider the following:
Remember, the most important factor is that the university and course align with your career goals and interests.
Now, let's take a closer look at the career landscape for you as a Computer Scientist. Upon completing your studies, your Computer Science qualification opens up a wide range of career paths in diverse sectors.
Below are some of the most sought-after career paths for a Computer Scientist:
Software Developer: A role that involves designing, coding, testing, and debugging software applications.
For all these jobs, you'll need to have strong technical skills, primarily in areas of programming, network systems, and data analysis. You should also have skills in:
Added to these, soft skills like teamwork and adaptability are prized assets in the ever-evolving field of computer science.
Computer science is a field of study that explores computing systems and technology. It involves the examination of software, hardware, the internet, and programming languages. The discipline combines aspects of mathematics and engineering to model, design, and test algorithms, which are step-by-step descriptions of how to accomplish tasks.
Computer science is about the study and application of computing technologies and methodologies. It involves understanding the design, application, and usage of computer systems, software, and networks. Areas of focus include programming, algorithms, data structures, artificial intelligence, and network architecture. Practically, it is the underpinning for virtually all modern technology applications like web browsing, video gaming and even digital financial systems.
An algorithm in computer science is a set of specific, step-by-step instructions or rules to be followed in calculations or problem-solving operations, especially by a computer. It is like a recipe that describes the exact steps required for the computer to solve a problem or reach a goal. These can range from simple processes, such as organising a list of numbers, to more complex procedures like image recognition and machine learning. Algorithms are fundamental to computer programming and software development.
With a Computer Science degree, you can work in a wide range of sectors such as software development, data analysis, cyber security, game design, IT consultancy, and website development. It also opens up opportunities for research-based roles in academia or private sectors. You may work in technology-related industries or apply your computational skills in banks, government agencies, education, healthcare or media companies. Also, a computer science degree can serve as a great foundation for entrepreneurial ventures.
Flashcards in Computer Science12290
Start learningWhat is the basic definition of computer programming?
Computer programming is the process of creating and implementing a set of instructions that tell a computer how to perform a task, akin to creating a recipe.
What are some of the most popular programming languages used in the industry today?
Python, Java, and C++ are some of the most popular programming languages used in the industry today.
Who is credited with writing the first computer program?
Ada Lovelace is credited with writing the first computer program.
What are some practical examples of computer programs used in daily life?
Practical examples of computer programs used in daily life include email services, word processing software, social media platforms, online banking apps, and weather forecasting software.
What are the two fundamental types of computer programming languages?
High-Level Languages and Low-Level Languages.
What characterises high-level and low-level languages?
High-level languages are closer to human language and include Python, while low-level languages are closer to machine language and include Assembly language.
Already have an account? Log in
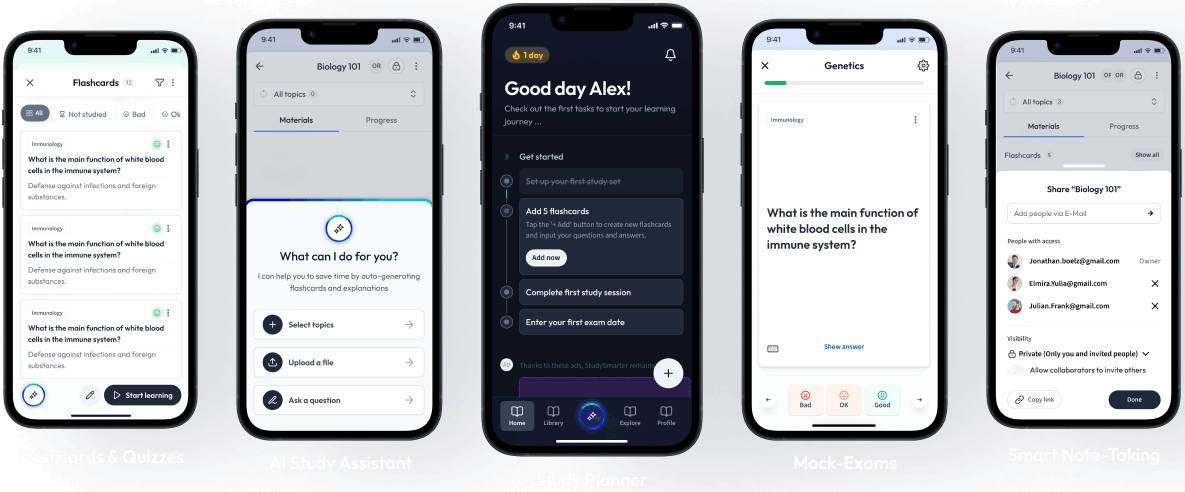
Open in AppHow would you like to learn this content?
How would you like to learn this content?
Free computer-science cheat sheet!
Everything you need to know on . A perfect summary so you can easily remember everything.
The first learning app that truly has everything you need to ace your exams in one place
Sign up to highlight and take notes. It’s 100% free.
Save explanations to your personalised space and access them anytime, anywhere!
Sign up with Email Sign up with AppleBy signing up, you agree to the Terms and Conditions and the Privacy Policy of StudySmarter.
Already have an account? Log in